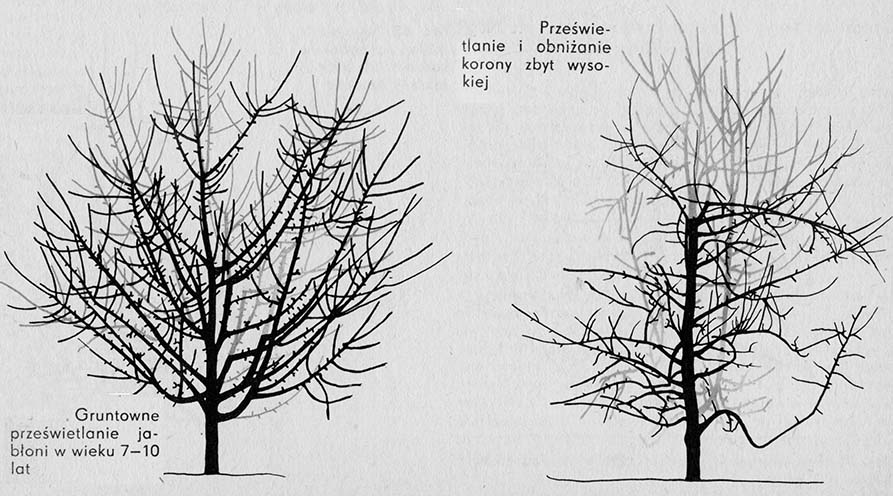
Nearly natural trees require more pruning when they reach 7-10 years of age. From now on, crowns need to be intensively x-rayed, and regulate their height and diameter.
Forming an almost natural crown, we obtain a conductor with branches embedded on it in the number from 10 into 15. This large number of branches is necessary on a young tree for its abundant fruiting. They don't mind how long the tree is young, and the size of the crown is small. As the tree grows, the crown becomes more and more denser and the branches need to be thinned gradually. We start thinning the branches 7-10 years after planting the trees. Cut 2-3 boughs each year, first from the lower whorls, later from the top. Permanently, no more than 6-8 branches should be left, grouped in two or three floors.
Branches and small shoots also need to be thinned. After cutting, the lowest branches should be half a meter from the ground. Every year, some of them lower to the ground under the mass of fruit and remain in this position. You have to remove them. We also remove branches and shoots from the center of the crown, so these, that intersect, overlap one another, they grow inward.
The earliest in 7 years after planting, and at the latest in 10 years you need to trim the guides of trees. In densely planted intensive orchards, trees should not be more than three meters high at the end of the growing season. The annual growth of trees in height is from 0,5 into 0,8 m. Therefore, during spring cutting, they have to be cut to the border 2,0-2,5 m. A good measure for trimming conductors is the reach of an outstretched hand of an adult worker standing next to a tree. It is approx 2,20 Metro. After trimming the conductors at this height, there are still small twigs above it, therefore the total height of the trees after pruning is 2,50 m.
Trees taller than the dimensions indicated above may expose the grower to serious trouble. Trees that are too tall cannot be sprayed effectively. On. In the upper branches of the apple trees, mildew and small fibrils appear, on the lower ones, it is difficult to control apple scab. Lower, overly shaded branches bear fruit poorly, giving rise to green and ungrown fruit. Pear trees that are too tall are less of a problem than apple trees, but here too it is difficult to care for and harvest the fruit.
Using cutting, we also correct the shape of the crowns and their diameter. In a densely planted orchard, the branches tend to grow stronger in the upper parts than in the lower parts., and this has a negative effect on the insolation of the lower branches. In 10-15 the years after the orchard was established need to be shortened for some, the tops of boughs growing more strongly, to restore the desired shape to the trees and keep the crowns in strictly defined sizes. The spacing of the trees determines the size of the crowns. At a distance of 6X4 m, the end diameter of the crowns must not exceed 4 m. Branches extending beyond this diameter, whether it is in the direction of the inter-row, whether in a row line, must be shortened.